Understanding Waist-to-Hip Ratio and Body Composition: A Comprehensive Guide

Explore the importance of waist-to-hip ratio and body composition, learn how to measure them, and understand their impact on overall health.
The waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and body composition are critical indicators of overall health and fitness. These measurements provide insights beyond what can be gleaned from body weight alone. This comprehensive guide will explore their importance, how to measure them, and their impact on your health.
What is Waist-to-Hip Ratio?
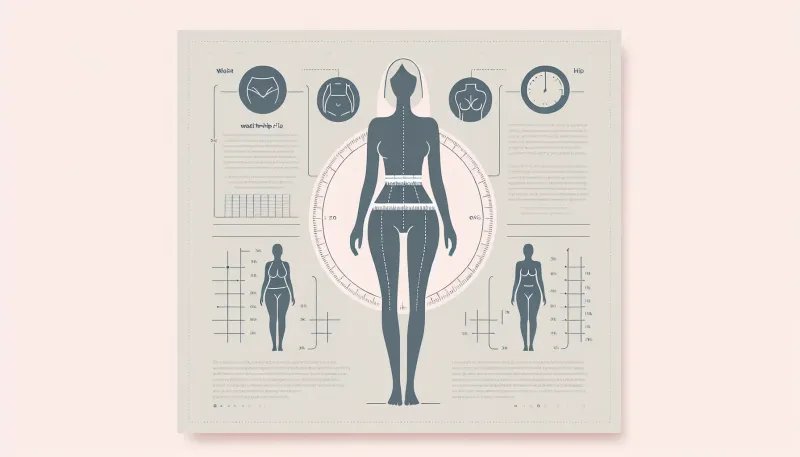
The waist-to-hip ratio is a simple measurement that compares the circumference of your waist to that of your hips. It is calculated by dividing the waist measurement by the hip measurement.
How to Measure Waist-to-Hip Ratio
To accurately measure your waist-to-hip ratio, follow these steps:
- Measure your waist: Use a measuring tape to measure the circumference of your waist at its narrowest point, typically just above your belly button.
- Measure your hips: Measure the circumference of your hips at their widest point, usually around the buttocks.
- Calculate the ratio: Divide your waist measurement by your hip measurement to get your WHR.
Interpreting Waist-to-Hip Ratio
The WHR is used to assess health risks associated with obesity and fat distribution:
- Men: A WHR of 0.9 or less is considered healthy, while a WHR greater than 1.0 indicates a higher risk of health issues.
- Women: A WHR of 0.85 or less is considered healthy, while a WHR greater than 0.85 may indicate a higher risk of health problems.
Understanding Body Composition
Body composition refers to the proportion of fat, bone, water, and muscle in your body. Unlike body mass index (BMI), which provides a general idea of body fat based on height and weight, body composition gives a more detailed picture of your physical state.
Components of Body Composition
Body composition is divided into two main components:
- Lean Mass: This includes muscles, bones, water, and other non-fat tissues.
- Fat Mass: This includes all the fat tissues in the body, both essential and storage fat.
Methods to Measure Body Composition
There are several methods to measure body composition:
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): This method uses electrical currents to estimate body composition. It's non-invasive and relatively accessible.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): DEXA scans provide detailed body composition information, including bone density and fat distribution, but can be expensive and require specialized equipment.
- Skinfold Calipers: This method involves measuring the thickness of skinfolds at specific body sites to estimate body fat percentage.
- Hydrostatic Weighing: Often considered the gold standard for measuring body composition, hydrostatic weighing involves submerging the body in water to measure body density and fat percentage.
Importance of Waist-to-Hip Ratio and Body Composition
Both WHR and body composition are vital for understanding health status and risks. Here’s why:
Health Implications
Studies have shown that WHR is closely linked to various health risks:
- Cardiovascular Disease: A higher WHR indicates more visceral fat, which is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Diabetes: Excess abdominal fat, reflected by a high WHR, is linked to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Overall Mortality: Research suggests that a higher WHR is correlated with a higher risk of premature death from various causes.
Fitness and Performance
Understanding your body composition can also help you improve your fitness and performance:
- Personalized Training: Knowing your lean mass and fat mass can help tailor your exercise program to build muscle or reduce fat effectively.
- Nutrition Planning: Detailed body composition analysis allows for more precise dietary planning to support your fitness goals.
Tips for Improving Waist-to-Hip Ratio and Body Composition
Improving your WHR and body composition involves a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Dietary Changes
Your diet plays a significant role in managing body composition and WHR:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Control Portion Sizes: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating and manage calorie intake.
- Reduce Processed Foods: Minimize the consumption of processed foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats.
Regular Exercise
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine is crucial for improving body composition:
- Strength Training: Engaging in strength training exercises helps build muscle mass and reduce body fat.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities such as running, cycling, and swimming improve cardiovascular health and burn calories.
- Consistency: Consistency is key. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact your WHR and body composition:
- Get Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support overall health and weight management.
- Manage Stress: High stress levels can contribute to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen. Practice stress-management techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is linked to increased abdominal fat and higher WHR.
Conclusion
Understanding waist-to-hip ratio and body composition is crucial for assessing health, setting fitness goals, and making informed lifestyle choices. By regularly monitoring these measurements and adopting healthy habits, you can improve your overall well-being and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Remember, it's essential to consult healthcare providers before making significant changes to your diet, exercise, or lifestyle. They can provide personalized advice and ensure that your plan is safe and effective for your unique needs.