Master Portion Control and Balanced Diet for a Healthier You
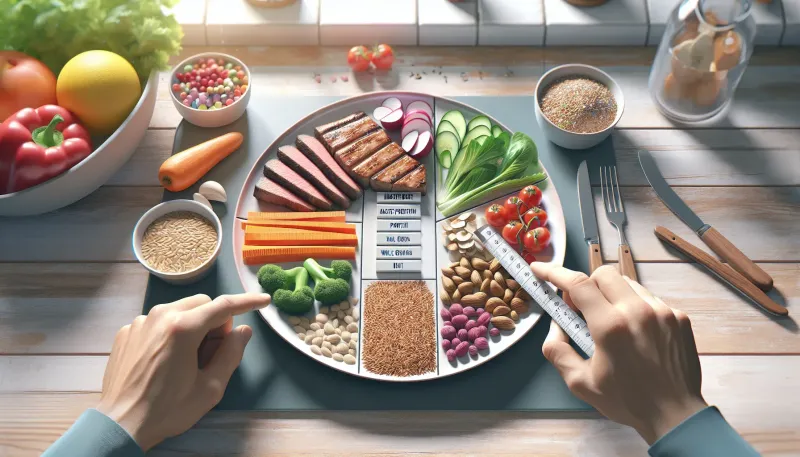

Learn the essentials of portion control and how a balanced diet can lead to a healthier lifestyle. Get tips and strategies to manage your food intake effectively.
Achieving a healthy lifestyle is often a topic laden with complex information, conflicting advice, and unattainable promises. However, focusing on two core principles—portion control and a balanced diet—can make a significant difference in your overall wellness. This article aims to demystify these concepts and provide practical strategies to incorporate them into your everyday life.
The Importance of Portion Control
Portion control refers to managing the quantity of food you consume in one sitting. While it may sound straightforward, it plays a critical role in weight management, nutritional balance, and overall health.
Understanding Portion Sizes
Unfortunately, modern serving sizes, especially in restaurants and packaged foods, often exceed the recommended portions. This leads to passive overeating, contributing to weight gain and other health issues.
Visual cues can be beneficial when determining portion sizes. For instance, a serving of protein should approximately match the size of your palm, while a serving of carbohydrates might be the size of your fist. Vegetables can usually fill half your plate without concern.
Tips for Effective Portion Control
- Use Smaller Plates: Smaller dishes can make portions appear larger, tricking your brain into feeling satisfied with less.
- Measure Your Food: Invest in a kitchen scale and measuring cups to accurately portion your meals at home.
- Read Nutrition Labels: Pay attention to the serving size and nutritional content to avoid unintentional overeating.
- Avoid Eating Directly from the Package: Always serve a portion on a plate instead, which helps visually assess how much you're consuming.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Slow down and savor each bite. Mindful eating helps recognize fullness cues, reducing the risk of overeating.
The Core Components of a Balanced Diet
Specific dietary needs can vary from person to person, but a balanced diet typically includes a variety of foods that provide essential nutrients. The key components to focus on are:
Macronutrients
Macronutrients, or "macros," consist of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a vital role in your body's functioning:
- Carbohydrates: Provide the primary source of energy. Opt for whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle repair and growth. Include lean meats, fish, beans, and nuts.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production and nutrient absorption. Focus on healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals are required in smaller amounts but are crucial for various bodily functions:
- Vitamins: Vital for immune function, energy production, and cell repair. Get a variety from fruits, vegetables, and fortified foods.
- Minerals: Support bone health, nerve function, and hydration. Sources include dairy products, leafy greens, and seafood.
Strategies for Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Achieving a balanced diet involves more than just choice; it requires routine and commitment. Here are actionable strategies to facilitate this:
Plan Your Meals
Meal planning can remove the guesswork and help you stay aligned with your nutritional goals. Preparing weekly menus ensures you include various food groups, avoid unhealthy options, and manage portion sizes efficiently.
Incorporate Whole Foods
Whole foods are minimally processed, providing more nutrients than refined or processed alternatives. Favor whole grains, fresh fruits, vegetables, and unprocessed proteins.
Stay Hydrated
Water is essential for virtually every bodily function, from digestion to temperature regulation. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, and more if you are physically active.
Limit Sugar and Salt Intake
Excessive sugar and salt can lead to various health issues, including hypertension and diabetes. Be mindful of their presence in processed foods and opt for alternatives like herbs and spices for flavoring.
Balancing Special Dietary Needs
Specific groups may require tailored dietary considerations:
Children
Children need nutrient-dense foods to support their growth and development. Include dairy for calcium, proteins for muscle development, and fruits and vegetables for vitamins.
Elderly
Seniors often face challenges such as reduced metabolism and nutrient absorption. A diet rich in fibers, proteins, and calcium is beneficial. Supplements might be necessary, but consult a healthcare professional for advice.
Athletes
Active individuals need higher calorie intake to fuel their energy demands. Focus on a balanced intake of carbs for energy, proteins for muscle repair, and fats for prolonged energy supply.
Conclusion
Mastering portion control and maintaining a balanced diet is fundamental for achieving and sustaining a healthier lifestyle. By understanding portion sizes, making conscious food choices, and tailoring your diet to suit your individual needs, you can significantly improve your overall well-being. Commit to these principles and incorporate the strategies discussed to see transformative results in your health journey.